It’s time for Cryptonite - our monthly roundup of all things crypto - with Dr. Tejaswi Nadahalli.
You can follow Tejaswi on twitter @nadahalli and he blogs at tejaswin.com
Tejaswi explains the concept of Bitcoin halving and its impact on miners. Every 10 minutes, a new block is mined, and the miner who mines the block is rewarded with new Bitcoin. The reward amount is halved approximately every four years. For instance, the reward was 6.25 Bitcoin per block until April 2020, and it is now 3.125 Bitcoin per block. This decrease in revenue for miners may lead some to shut down their operations, while profitable miners remain. He argues that this is not a bad thing, as the value of Bitcoin will eventually increase to cover the costs of mining, including electricity and hardware. Additionally, transaction fees will become more significant sources of revenue for miners. Tejaswi further suggests that the fee split may eventually reverse, with 80% coming from transaction fees and 20% from new Bitcoin rewards, and there are signs that point to this direction.
We discuss the ongoing research to build more powerful smart contracts on Bitcoin, which will pay higher fees due to increased economic activity. This trend of more transactions with higher economic density is reducing the significance of the Bitcoin security budget issue. Tejaswi then mentions the varying cost structures of Bitcoin miners around the world, with some, like Marathon and Riot in the US, providing clear statements. The difficulty of mining Bitcoin has been increasing, and while this may indicate lowering costs for some miners, the profitability of mining is currently being impacted by rising costs and competition from AI mining. We question whether mining Bitcoin or setting up a data center for AI training will be more lucrative in the future.
We discuss the importance of reliability in AI training and the demand for reliable hardware. Tejaswi explains that AI training jobs have higher standards and require reliable hardware, up time, and quality of service. He then goes on to describe how the crypto marketplace is being constructed for AI training, with examples of companies like SingularityNet, Akash Network, and Render. He mentions that these marketplaces are not always reliable, leading to frustration from AI job providers. Tejaswi also compares the reliability standards of AI training to Bitcoin mining and human flourishing, with electricity being better spent on human flourishing and AI training before Bitcoin mining. He also touches on the topic of government regulators' concerns about AI training consuming all the electricity in the world and the strength of the anti-nuclear power lobby.
Shyam discusses the failure of governments to embrace nuclear power and new technologies, despite their potential for abundant energy. He recalls a time when scientists projected an energy surplus, leading to the encouragement of new electrical appliances. However, this did not come to fruition due to the continued blocking of innovation. Shyam also touches on the subject of AI efficiency and the importance of focusing on productivity rather than shutting down innovation. Additionally, the video covers the recent trend of meme coins on the Solana blockchain, which have become popular due to their low transaction fees but have caused issues for the blockchain itself.
Tejaswi discusses the issues Solana faced in April 2024 due to a massive influx of transactions. Validators on the Solana network were unable to handle the load, causing both networking and consensus failures. The network collapsed under the weight of incoming connections, leading to a 20% success rate for transactions. In response, a new currency called "ore" was created, incentivizing failed transactions. Solana's engineers are working on updating their networking stack and consensus algorithm to address these issues, but the fee structure remains broken. The debate over what constitutes a "serious" transaction versus "spam" is ongoing in the Bitcoin community, with no clear winner.
Tejaswi discusses the concept of limited block space in cryptocurrencies, specifically focusing on Bitcoin. He explains that due to the finite block space, fees will eventually rise to match the demand. Bitcoin's block space is limited to 1 MB every 10 minutes, which is set in stone due to its difficulty adjustment. Ethena, a deeply venture-backed project, is introduced as a controversial venture that tokenizes the basis trade. Ethena buys Ethereum spot and sells futures contracts at a higher price, pocketing the basis difference when the futures contract matures. Shyam notes that there are counterparty risks involved and the trade seems elementary, but the tokenization of it is fairly obvious. The discussion then shifts to the fair funding rate in the futures market and the importance of it not exceeding the risk-free rate.
We discuss the concept of a risk-free rate in the crypto world, comparing it to the 5% yield on US Treasuries — the risk-free rate for crypto should be higher due to counterparty risk and market instability.
We discuss the ongoing court case involving Tornado Cash. Shyam finds it intriguing how these events are interconnected, with one leading to another in a long chain of events. Tornado Cash is an open-source privacy protocol, but it also had a token called TORN, which gave financial incentives to those who deployed it on the blockchain. This added layer of financial motivation complicates the situation and raises questions about the developers' intentions. Tejaswi expresses support for the open-source code but hesitates to defend the financial motivations behind it. The discussion also touches upon the ongoing debate regarding privacy and its implications for illegal activities.
Tejaswi discusses the regulatory issues surrounding Uniswap, a decentralized finance protocol. For a long time, Uniswap's UNI token had no value and was not required for using the platform. However, earlier this year, Uniswap enabled a fee switch, which sends a portion of trading commissions to UNI token holders, including Uniswap's organization. This development raised concerns from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which accused Uniswap of operating an unregistered exchange. Uniswap argues that they only have the ability to enable the fee switch and cannot stop unregistered listings, but they are still happy to take commissions from these trades. Tejaswi questions whether Uniswap or the token creators are the bad actors and expresses skepticism about the SEC's motives, as they have already lost a case against Ripple. He also mentions that the SEC has settled with other crypto projects in the past and suggests that they may be looking for a payday in the Uniswap case. If the SEC loses, it could set a precedent for other decentralized finance projects.
Tejaswi discusses the concept of Babylon, an innovation in the crypto world that focuses on holding bad actors accountable by exposing their private keys if they fail to honor transactions. Bitcoin, which operates in its own insular ecosystem, doesn't have a built-in mechanism to force operators to return funds, making it easy for them to censor or blacklist users. Babylon aims to address this issue by enabling the creation of a separate ecosystem with smart contracts, where users can trustlessly enter and exit the system, forcing operators to honor transactions and return funds or risk having their private keys exposed. Tejaswi finds this innovation fascinating, as it shows that even after 15 years of Bitcoin's existence, new cryptographic constructs continue to emerge.
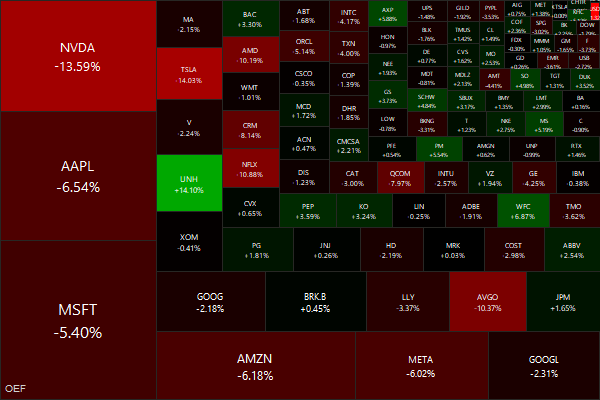
Markets this Week
Israel/Iran droned on and markets went from pricing three Fed rate cuts this year to just one…
… what NVDA giveth, NVDA taketh away.
More here: country ETFs, fixed income, currencies and commodities.
Links
Crypto
Mango Markets Exploiter Avi Eisenberg Found Guilty of Fraud and Manipulation. Faces 20 years in prison for his $110 million heist. He tried to argue that "code is law", and that his actions were legal as they were allowed by the project's smart contracts, jurors ultimately agreed with prosecutors that his manipulation of token prices constituted fraud. (coindesk, web3isgoinggreat)
Quantifying the Cost to Attack Bitcoin and Ethereum (SSRN)
Why Bitcoin and Ethereum Differ in Transaction Costs (SSRN)
Investing & Economy
The combination of strong US growth and sticky inflation is raising the odds the Federal Reserve hikes rather than cuts interest rates. (yahoo)
Details about Jane Street's top-secret $1 billion trade revealed in court. And it involves option trading in India. (businessinsider)
Mario Draghi: Radical Change—Is What Is Needed (geopolitique)
EU Goes on China Trade Offensive After Getting ‘Played’ (bloomberg)
The world turned away from free trade decades ago. The large, persistent surpluses that have characterized global trade since the 1980s are largely the consequences of beggar-thy-neighbor trade policies aimed at boosting domestic growth a the expense of trade partners.
Nearly fifty years after the “Japan shock,” today’s global automotive industry confronts a far more systemic upheaval—what we could term the “Chinese electric vehicle (EV) shock.” (phenomenalworld)
Trump trade advisers plot dollar devaluation (politico)
Overall, America taxes the rich and corporations similarly to OECD. But tax rates on middle- and low-earners have collapsed over the years, producing a more progressive tax code. Total revenues have remained mostly steady, with the overall burden shifting up the income ladder.